Difference between revisions of "Visual content reproduction"
| (15 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Website | {{Website | ||
|headline=VisualContentReproduction | |headline=VisualContentReproduction | ||
| − | |coordhead= | + | |coordhead=3.000, 49.252, 0.000 |
| − | |image1= | + | |image1=/wiki/images/VisualContentReproduction.png |
|coordimg1=0, 0, 0 | |coordimg1=0, 0, 0 | ||
|simploduction=<ul> | |simploduction=<ul> | ||
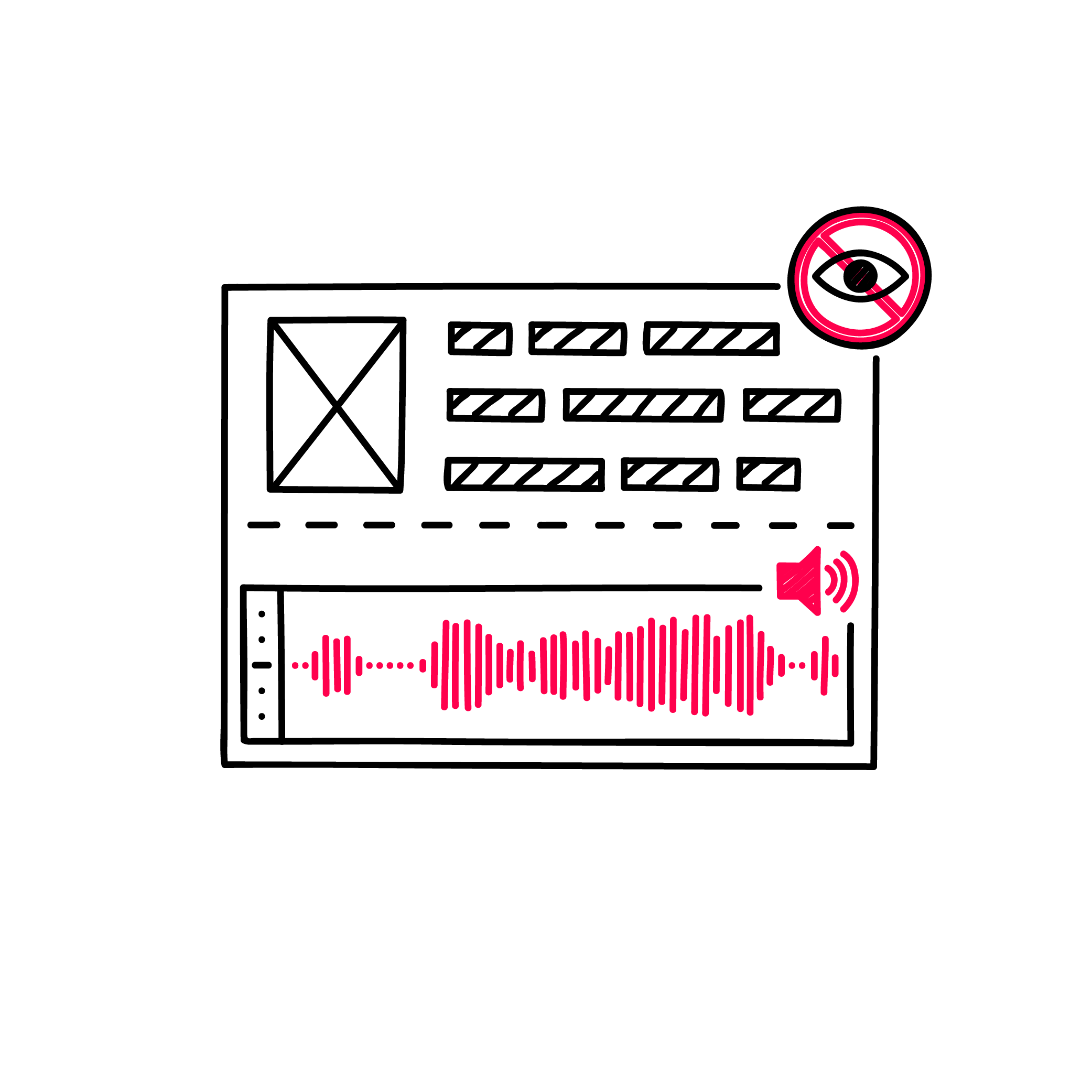
| − | <li> | + | <li>How to deal with visible information.</li> |
| − | <li>People with limited or no sight | + | <li>People with limited or no sight depend on audible or tactile information.</li> |
| − | <li>Screen readers or | + | <li>Screen readers or braille displays are used for this purpose.</li> |
| − | <li>Written information should | + | <li>Written information should be embedded in a way that can be understood by these devices.</li> |
<li>Non-textual visible content should be provided with captions.</li></ul> | <li>Non-textual visible content should be provided with captions.</li></ul> | ||
|coordsimplo=0, 0, 0 | |coordsimplo=0, 0, 0 | ||
| − | |testimonial= | + | |testimonial= |
| + | Ilya is blind [...] <i>(and)</i> uses a screen reader and mobile phone to access the web. Both her screen reader and her mobile phone accessibility features provide her with information regarding the device’s operating system, applications, and text content in a speech output form. | ||
| + | When accessing web content, the screen reader indicates aloud the structural information on a webpage such as headings, column and row headers in tables, list items, links, form controls, and more that enable her to better navigate the page, complete and submit forms, and access information in an effective manner. She is able to listen to and understand speech output at a very high speed. Ilya encounters problems when websites are not properly coded and do not include alt text descriptions on images. These sites are unnavigable and require large amounts of time to read text from the top of the page to the bottom without navigation cues. Occasionally she finds herself trapped in areas on a webpage unable to move to another area and must abandon the page altogether. | ||
| + | <a href="https://www.w3.org/WAI/people-use-web/user-stories/#accountant">Source</a> | ||
|coordtesti=0, 0, 0 | |coordtesti=0, 0, 0 | ||
| − | |belongsto= | + | |belongsto=Sight |
|contains=Visual_content_reproduction_References | |contains=Visual_content_reproduction_References | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | == | + | |
| − | * | + | __TOC__ |
| − | * People with limited or no sight | + | |
| − | * Screen readers or | + | [[File:VisualContentReproduction.png|400px|none|Illustration Visual content reproduction]] |
| − | * Written information should | + | <div class="text_content"> |
| + | ==Overview== | ||
| + | * How to deal with visible information. | ||
| + | * People with limited or no sight depend on audible or tactile information. | ||
| + | * Screen readers or braille displays are used for this purpose. | ||
| + | * Written information should be embedded in a way that can be understood by these devices. | ||
* Non-textual visible content should be provided with captions. | * Non-textual visible content should be provided with captions. | ||
| − | == | + | ==User story== |
| − | + | Ilya is blind [...] ''(and)'' uses a screen reader and mobile phone to access the web. Both her screen reader and her mobile phone accessibility features provide her with information regarding the device’s operating system, applications, and text content in a speech output form. | |
| + | When accessing web content, the screen reader indicates aloud the structural information on a webpage such as headings, column and row headers in tables, list items, links, form controls, and more that enable her to better navigate the page, complete and submit forms, and access information in an effective manner. She is able to listen to and understand speech output at a very high speed. Ilya encounters problems when websites are not properly coded and do not include alt text descriptions on images. These sites are unnavigable and require large amounts of time to read text from the top of the page to the bottom without navigation cues. Occasionally she finds herself trapped in areas on a webpage unable to move to another area and must abandon the page altogether. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Source: https://www.w3.org/WAI/people-use-web/user-stories/#accountant | ||
| − | ==[[Visual_content_reproduction_References|Visual content reproduction | + | ==[[Visual_content_reproduction_References|References for Visual content reproduction]]== |
===[[Visual_content_reproduction_References#General|General]]=== | ===[[Visual_content_reproduction_References#General|General]]=== | ||
===[[Visual_content_reproduction_References#Captions|Captions]]=== | ===[[Visual_content_reproduction_References#Captions|Captions]]=== | ||
===[[Visual_content_reproduction_References#Text_Alternatives|Text Alternatives]]=== | ===[[Visual_content_reproduction_References#Text_Alternatives|Text Alternatives]]=== | ||
===[[Visual_content_reproduction_References#Audio_Description|Audio Description]]=== | ===[[Visual_content_reproduction_References#Audio_Description|Audio Description]]=== | ||
| + | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 15:54, 9 June 2021
| headline | VisualContentReproduction |
|---|---|
| headline coordinates | 3.000, 49.252, 0.000 |
| image | /wiki/images/VisualContentReproduction.png |
| image coordinates | 0, 0, 0 |
| simple introduction |
|
| simple introduction coordinates | 0, 0, 0 |
| testimonial | Ilya is blind [...] (and) uses a screen reader and mobile phone to access the web. Both her screen reader and her mobile phone accessibility features provide her with information regarding the device’s operating system, applications, and text content in a speech output form.
When accessing web content, the screen reader indicates aloud the structural information on a webpage such as headings, column and row headers in tables, list items, links, form controls, and more that enable her to better navigate the page, complete and submit forms, and access information in an effective manner. She is able to listen to and understand speech output at a very high speed. Ilya encounters problems when websites are not properly coded and do not include alt text descriptions on images. These sites are unnavigable and require large amounts of time to read text from the top of the page to the bottom without navigation cues. Occasionally she finds herself trapped in areas on a webpage unable to move to another area and must abandon the page altogether. <a href="https://www.w3.org/WAI/people-use-web/user-stories/#accountant">Source</a> |
| testimonial coordinates | 0, 0, 0 |
| links to | |
| belongs to | Sight |
| contains | Visual_content_reproduction_References |
Overview[edit]
- How to deal with visible information.
- People with limited or no sight depend on audible or tactile information.
- Screen readers or braille displays are used for this purpose.
- Written information should be embedded in a way that can be understood by these devices.
- Non-textual visible content should be provided with captions.
User story[edit]
Ilya is blind [...] (and) uses a screen reader and mobile phone to access the web. Both her screen reader and her mobile phone accessibility features provide her with information regarding the device’s operating system, applications, and text content in a speech output form. When accessing web content, the screen reader indicates aloud the structural information on a webpage such as headings, column and row headers in tables, list items, links, form controls, and more that enable her to better navigate the page, complete and submit forms, and access information in an effective manner. She is able to listen to and understand speech output at a very high speed. Ilya encounters problems when websites are not properly coded and do not include alt text descriptions on images. These sites are unnavigable and require large amounts of time to read text from the top of the page to the bottom without navigation cues. Occasionally she finds herself trapped in areas on a webpage unable to move to another area and must abandon the page altogether.
Source: https://www.w3.org/WAI/people-use-web/user-stories/#accountant